cannabinoids
THC O – What is THC-O Acetate?
THC-O’s is increasingly being known for its potency and its legal status. Research has found that it’s roughly three times stronger than conventional THC. It has been called “the psychedelic cannabinoid” for its hallucinogenic effects. Because it’s derived from federally legal hemp, THC-O products are becoming increasingly popular in the states where consumers don’t have access to legal, state-licensed Cannabis products.
And now that delta-8 THC, its trendy cousin, has been outlawed in some states across the country and flagged by the DEA, THC-O is becoming the next “best” thing.
While THC-O products like vape carts and edibles are available for purchase online or in stores, both their legal status and their safety remain unknown.
Read on to learn more about THC-O acetate, its possible benefits, and the risks you should be aware of before trying it.
What is THC-O?
Although many of us only recently heard about THC-O, the US military began studying its effects as long ago as 1949.
THC-O didn’t appear on the DEA’s radar until roughly 30 years later. In 1978, DEA agents discovered a clandestine lab in Jacksonville, Florida, had combined a Marijuana extract with acetic anhydride. But over the following 10 years, THC-O did not enter the illegal/legal drug market. Since it didn’t seem to be a growing problem, the FDA declined further investigation into the unusual substance.
Today the production of THC-O acetate is rising concern among some in the state-licensed cannabis industry. To generate the molecule, a highly-flammable (And Dangerous) compound called acetic anhydride is added to THC molecules. The process involves a series of extractions that begin with hemp. First, CBD is extracted from raw hemp. Then delta-8 THC is extracted from the CBD. Finally, acetic anhydride is added to the delta-8 THC molecules to make what is known as THC-O acetate.
Experts say this process should only be done under controlled laboratory conditions, due to the major health risks involved with the extraction process.
What is the difference between THC & THC-O?
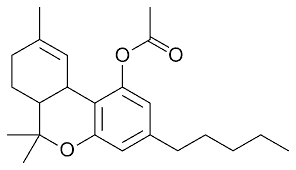
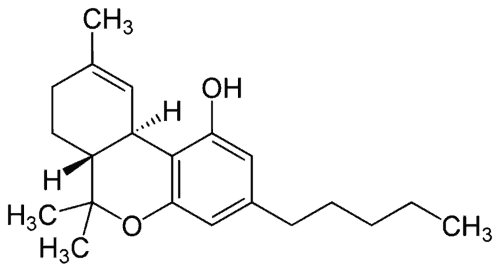
Here’s a picture of a regular old THC molecule:
Now here is a picture of the THC-O molecule:
The biggest difference between the two pictures (aside from the lack of Hs and Cs and 3s) is In the top picture of the THC molecule, there’s an OH. In the bottom picture of the THC-O molecule, there’s an O and a set of lines. That new set of lines is the acetate molecule (the “A” in ATHC).
It’s the addition of that new molecule that sets ATHC apart from regular THC and makes it completely unique.
What are the effects of THC-O?
Many describe the effects of THC-O as very spiritual and almost psychedelic. Some people even describe the high as to LSD and shrooms.
One thing of note is that, like edibles, you’ll have to wait 20 to 30 minutes before you feel its effects. This is because your body has to separate (digest) the acetate molecule from the THC molecule.
Is it Safe?
A lack of research and a profound lack of regulation based on factual data means that the safety of THC-O acetate are unknown.
Beyond its potency, researchers have concluded that THC-O acetate is a “prodrug,” meaning that the compound is not activated until it has been metabolized. Typically, It may take about 20 to 30 minutes to kick in.
James Stephens is a cannabis researcher and chemist. He’s investigated the effects of THC-O as part of his work for Iron Light. Stephens cautions that there are wide variations in product quality right now, early in the compound’s commercial emergence.
Since THC-O is a fully synthetic cannabinoid made by using highly dangerous substances, it is recommended to use caution when consuming THC-O products. If you do however try it, we recommend to only buy it from trusted sellers.


Comments are closed.